d & f-Block Formulas
Are you fed up with the concept of d & f-Block and need any assistance to learn and understand the topic? You have stepped into the correct page. Here, we have curated the list of d & f-Block formulas that help all students to get a great hold on the concept of d & f-Block. This formulae sheet of d & f-Block also aids at the time of the revision process and exam preparation process. So, avail this d & f-Block formulas list from here and grasp the knowledge of the entire concept easily.
Solve your chemistry problems fastly and efficiently taking the help of Chemistry Formulas and learn about the Concepts without much effort.
Tables & Cheat Sheet for d & f-Block Formulas
Ace up your preparation & solve all the problems related to this concept by using the given d & f-Block formulae sheet or tables. D & F-Block concept is no more considered as a difficult topic for students after referring and memorizing the provided d & f-Block formulas using the sheet or tables. Check out the important formulas of d & f-Block and understand the concept in a better way.
1. d-block elements are called transition elements because their properties are in between those of s-block and p-block elements.
2. General electronic configuration of d-block elements is (n – 1 )d1-10 ns1-2 & f-block is (n – 2)f1-14 (n – 1) d0-1 ns2
3. There are four transition series, called 3d, 4d, 5d and 6d series. The elements present in them are: 3d(21Sc – 30Zn), 4d (39Y – 48Cd), 5d (57La, 72HF – 80Hg), 6d starts with 89Ac but is incomplete.
4. The elements of the 1st transition series are:
21Sc, 22Ti, 23V, 24Cr, 25Mn, 26Fe, 27Co, 28Ni, 29Cu, 30Zn
5. Some transition elements showing exceptional electronic configuration are:
24Cr (3d5 4s1), 29Cu(3d10, 4s1),
42Mo (4d5 5s1), 44Ru(4d7 5s1),
45Rh (4d8 5s1), 46Pd(4d10, 5s0),
47Ag (4d10 5s1), La(5d1, 7s2),
78Pt (5d9 6s1), 79Au(5d10, 6s1),
6. Zn, Cd and Hg are not considered as transition elements because their d- orbitals are completely filled. Unlike other transition metals, they are not hard because they do not contain unpaired electrons and metallic bond in them is weak.
7. Greater the number of unpaired electrons, stronger is the metallic bond and hence higher is the melting point. That is why melting points first rise to a maximum and then fall.
8. The first ionisation energy of 5d elements is higher than those of 3d and 4d elements due to intervening 4 f electrons thereby weakening the shielding effect.
9. IE1 + IE2 for Ni is less than that of Pt, Hence Ni (II) compounds are more stable than Pt (II) compounds. IE1 + IE2 + IE3 + IE4 for Pt is greater than that Ni. Hence Pt (IV) compounds are more stable than Ni (IV) compounds.
10. The maximum oxidation state shown by transition element is + 8 (by Rh.) Os shows maximum of + 7.
11. The catalyst used in Fischer-Tropsch process for synthesis of gasoline (petrol) is Cobalt- Thorium.
12. Cu (II) salts absorb red wavelength for d-d transition and look blue (because red and blue are complementary colour).
13. The complex [Ti(H2O)6]3+ absorbs yellow wavelength from visible light. Hence blue and red are transmitted. Their mixed effect is purple.
14. Sc3- and Ti4- are colourless as they have completely empty d – orbitals. Cu+ and Zn2- are colour less as they have completely filled d-orbitals.
15. Substances containing unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. Those containing no unpaired electron are diamagnetic.
16. Magnetic moment, µ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\) B.M. where n = no. of unpaired electrons
and 1 B.M. = \(\frac{\mathrm{eh}}{4 \pi \mathrm{mc}}\).
17. Iron, cobalt and nickel are called ferrous metals; copper, silver and gold are called coinage metals.
Potassium dichromate
Preparation:
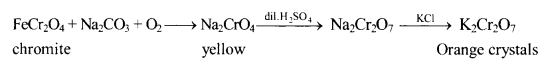
Properties:
Strong Oxidising agent
18. Potassium dichromate on heating gives K2CrO4, Cr2O3 and O2.
19. Aqueous solution of K2Cr2O7 contains Cr2O72- as well as CrO42- ions is equilibrium.
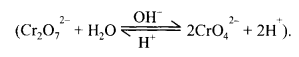
On adding alkali, it shifts forward and is yellow. On adding acid, it shifts backward and is orange red.
20. On heating KCI with K2CrO7 and cone. H2SO4, orange red vapours evolved are due to chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2).
Potassium permangnate
Preperation:
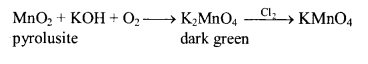
Properties
Acidified KMnO4 oxidises Fe2+ to Fe3+
21. Electrolysis of potassium manganate (K2MnO4) gives potassium permanganate (KMnO4).
22. KMnO4 on heating gives K2MnO4, MnO2 and O2.
23. Alkaline KMnO4 sol. is called Baeyer’s reagent. It oxidizes unsaturated compounds and as a result its own pink colour is discharged.
24. CrO42- as well as MnO4– ions have tetrahedral structure.
f-Block: Lanthanides and Actinides
1. The general electronic configuration of inner transition elements of (f-block elements) is (n – 2) f0-14 (n – 1)d0-1 ns2.
2. Most stable oxidation state of lanthanides is +3. Those having +2 (e.g Sm2+, Eu2+ and Yb2+) or + 4 (e.g. Ce4+) tend to revert to +3. Flence former act as reducing agents while the latter as oxidizing agent.
3. 40Zr and 72Hf have nearly same size because of lanthanide contraction before Hf (i.e. atomic radii 22Ti < 40Zn72 ≃ Hf). Similarly, 23 < 41Nb ≃ 73Ta.
4. The decrease in radius for 14 lanthanides (58Ce to 71Lu) is only 15 pm (188 to 173 pm).
5. The maximum oxidation state show by actinides is +7. (U, Np and Pu show oxidation state of +6).
Explore all chemistry formulas under one roof i.e., Onlinecalculator.guru, and score high in the subject examinations.