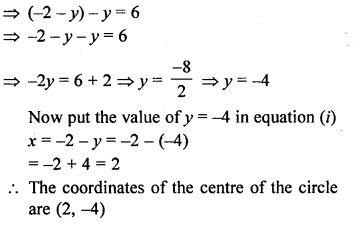ML Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 19 Coordinate Geometry
EXERCISE 19.1
Question 1.
Find the co-ordinates of points whose
(i) abscissa is 3 and ordinate -4.
(ii) abscissa is – \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)and ordinate 5.
(iii) whose abscissa is -1\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) and ordinate -2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) .
(iv) whose ordinate is 5 and abscissa is -2
(v) whose abscissa is -2 and lies on x-axis.
(vi) whose ordinate is \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) and lies on y-axis.
Solution:

Question 2.
In which quadrant or on which axis each of the following points lie?
(-3, 5), (4, -1) (2, 0), (2, 2), (-3, -6)
Solution:

Question 3.
Which of the following points lie on
(i) x-axis? (ii) y-axis?
A (0, 2), B (5, 6), C (23, 0), D (0, 23), E (0, -4), F (-6, 0), G (√3,0)
Solution:
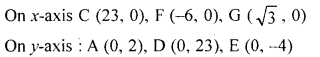
Question 4.
Plot the following points on the same graph paper :
A (3, 4), B (-3, 1), C (1, -2), D (-2, -3), E (0, 5), F (5, 0), G (0, -3), H (-3, 0).
Solution:
- Quadrilaterals Class 9 Formulas
- Probability Class 9 Formulas
- Polynomials Class 9 Formulas
- Number Systems Class 9 Formulas
- Lines and Angles Class 9 Formulas
- Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 9 Formulas
- Introduction To Euclid’S Geometry Class 9 Formulas
- Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Formulas
- Constructions Class 9 Formulas
- Circles Class 9 Formulas
- Areas Of Parallelograms and Triangles Class 9 Formulas
- Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 Formulas
- Herons Formula Class 9 Formulas
- Triangles Class 9 Formulas
- Statistics Class 9 Formulas
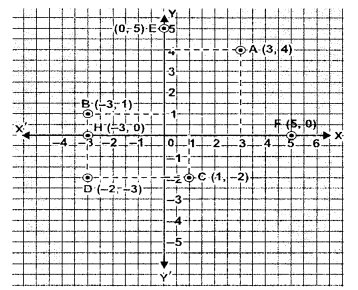
Question 5.
Write the co-ordinates of the points A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H shown in the adjacent figure.
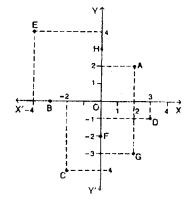
Solution:
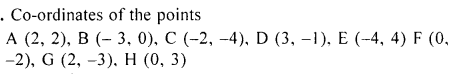
Question 6.
In which quadrants are the points A, B, C and D of problem 3 located ?
Solution:
A Lies in the first quadrant, B lies on x-axis C lies in the third quadrant and D lies in the fourth quadrant.
Question 7.
Plot the following points on the same graph paper :

Solution:
Question 8.
Plot the following points on the same graph paper.
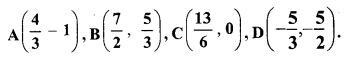
Solution:
Question 9.
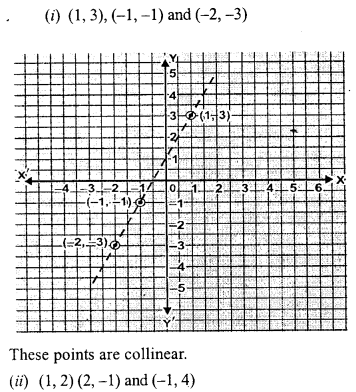
Plot the following points and check whether they are collinear or not:
(i) (1,3), (-1,-1) and (-2,-3)
(ii) (1,2), (2,-1) and (-1, 4)
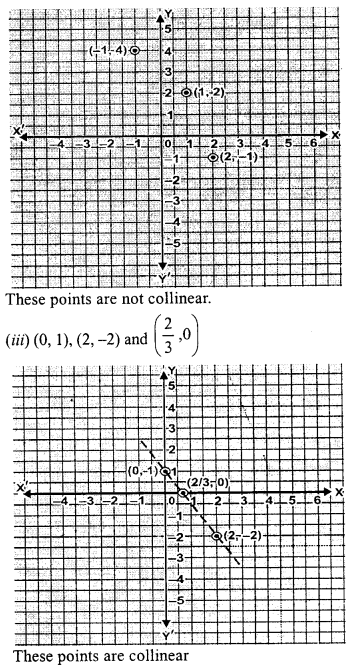
(iii) (0,1), (2, -2) and (\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) ,0)
Solution:
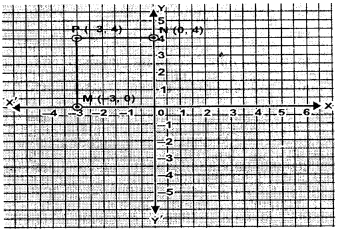
Question 10.
Plot the point P(-3, 4). Draw PM and PN perpendiculars to x-axis and y-axis respectively. State the co-ordinates of the points M and N.
Solution:
![]()
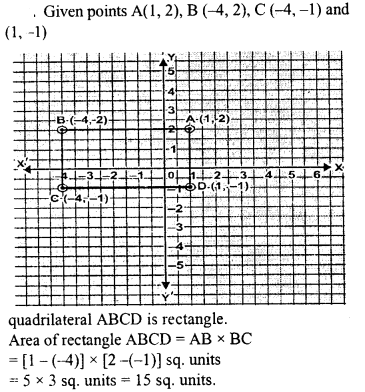
Question 11.
Plot the points A (1,2), B (-4,2), C (-4, -1) and D (1, -1). What kind of quadrilateral is ABCD ? Also find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD.
Solution:
Question 12.
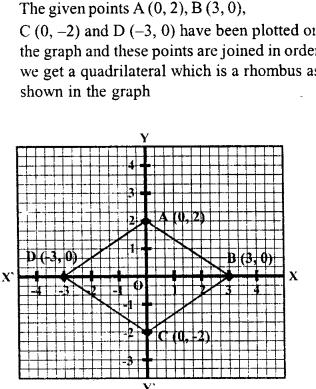
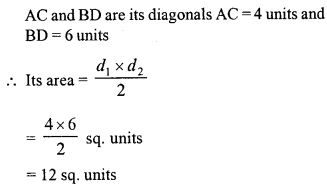
Plot the points (0,2), (3,0), (0, -2) and (-3,0) on a graph paper. Join these points (in order). Name the figure so obtained and find the area of the figure obtained.
Solution:
Question 13.
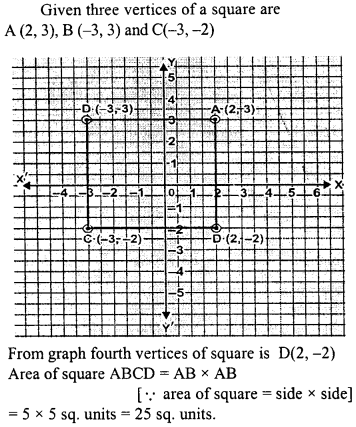
Three vertices of a square are A (2,3), B(-3, 3) and C (-3, -2). Plot these points on a graph paper and hence use it to find the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex. Also find the area of the square.
Solution:
Question 14.
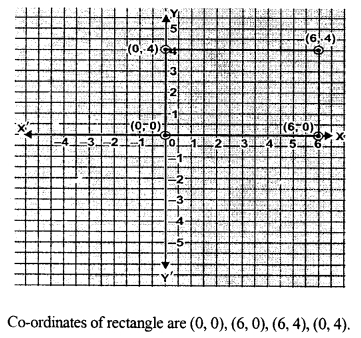
Write the co-ordinates of the vertices of a rectangle which is 6 units long and 4 units wide if the rectangle is in the first quadrant, its longer side lies on the x-axis and one vertex is at the origin.
Solution:
![]()
Question 15.
Repeat problem 12 assuming that the rectangle is in the third quadrant with all other conditions remaining the same.
Solution:
A rectangle which is 6 unit long and 4 units wide and this rectangle is in the third quadrant.
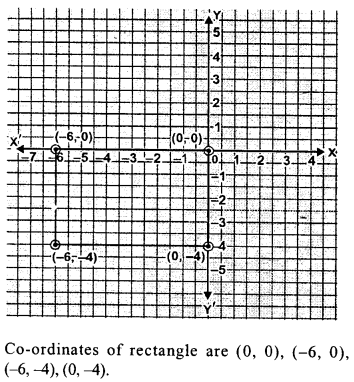
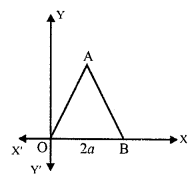
Question 16.
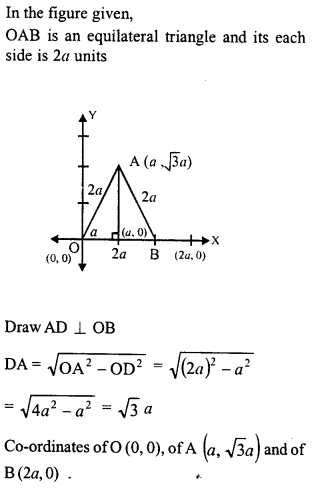
The adjoining figure shows an equilateral triangle OAB with each side = 2a units. Find the coordinates of the vertices.
Solution:
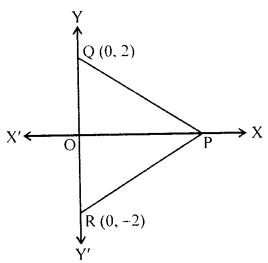
Question 17.
In the given figure, APQR is equilateral. If the coordinates of the points Q and R are (0, 2) and (0, -2) respectively, find the coordinates of the point P.
Solution:
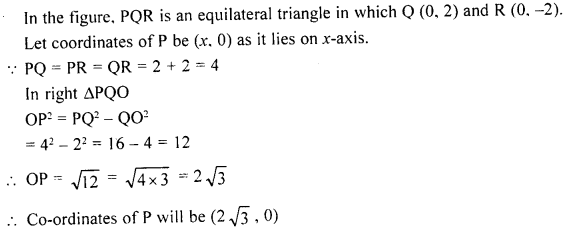
EXERCISE 19.2
Question 1.
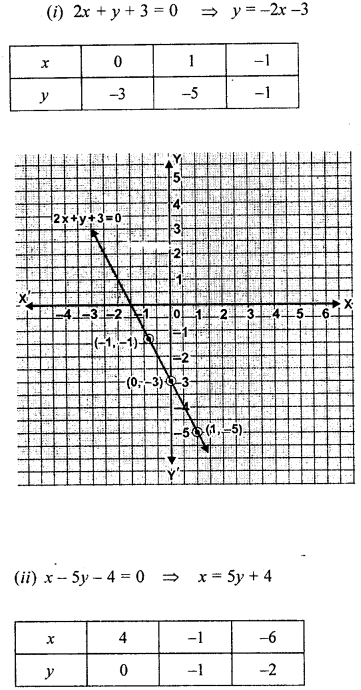
Draw the graphs of the following linear equations :
(i) 2x + + 3 = 0
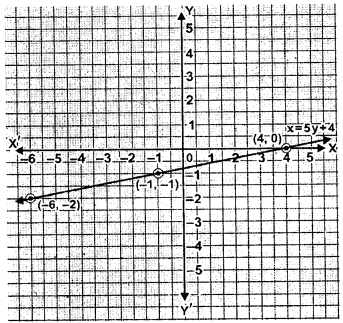
(ii) x- 5y- 4 = 0
Solution:
Question 2.
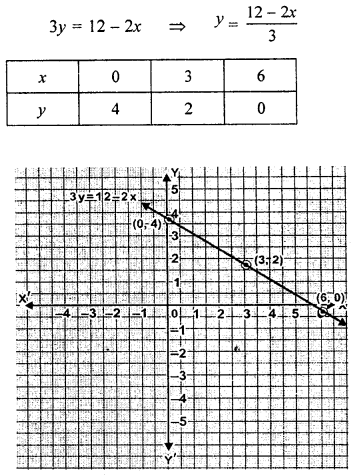
Draw the graph of 3y= 12 – 2x. Take 2cm = 1 unit on both axes.
Solution:
Question 3.
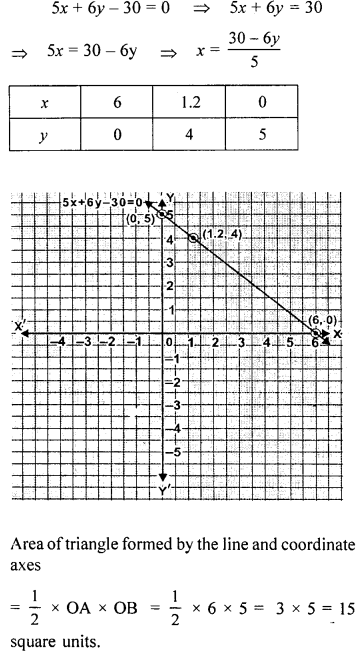
Draw the graph of 5x + 6y – 30 = 0 and use it to find the area of the triangle formed by the line and the co-ordinate axes.
Solution:
Question 4.
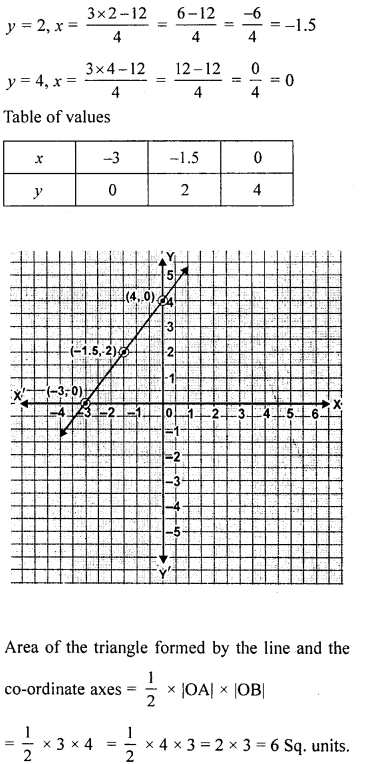
Draw the graph of 4x- 3y + 12 = 0 and use it to find the area of the triangle formd by the line and the co-ordinate axes. Take 2 cm = 1 unit on both axes.
Solution:
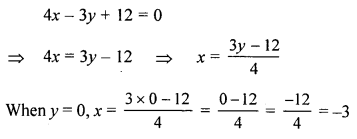
Question 5.
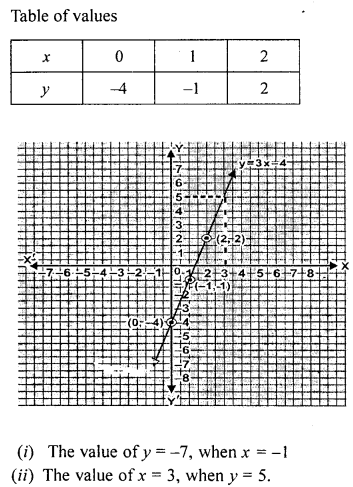
Draw the graph of the equation y = 3x – 4. Find graphically.
(i) the value of y when x = -1
(ii) the value of x when y = 5.
Solution:
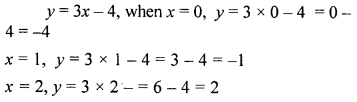
Question 6.
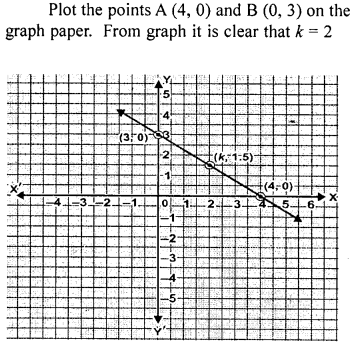
The graph of a linear equation in x and y passes through (4, 0) and (0, 3). Find the value of k if the graph passes through (A, 1.5).
Solution:
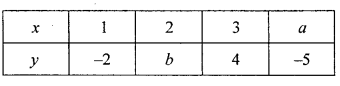
Question 7.
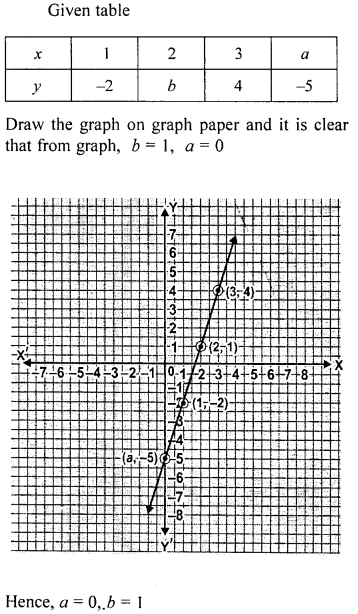
Use the table given alongside to draw the graph of a straight line. Find, graphically the values of a and b.
Solution:
EXERCISE 19.3
Question 1.
Solve the following equations graphically: 3x – 2y = 4, 5x – 2y = 0
Solution:
![]()
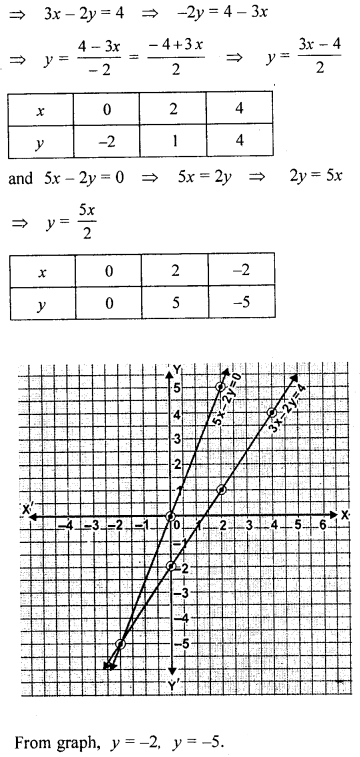
Question 2.
Solve the following pair of equations graphically. Plot at least 3 points for each straight line 2x – 7y = 6, 5x – 8y = – 4
Solution:
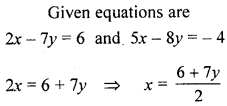
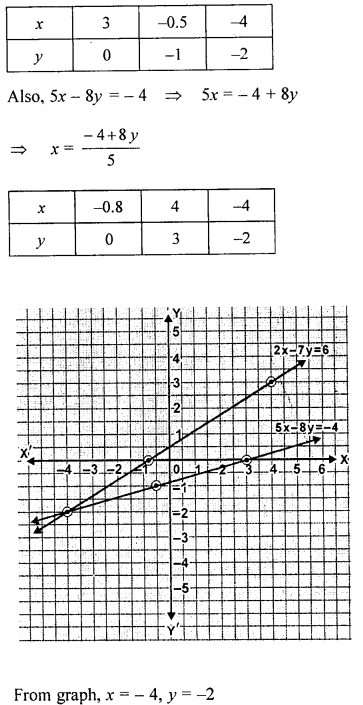
Question 3.
Using the same axes of co-ordinates and the same unit, solve graphically.
x+y = 0, 3x – 2y = 10
Solution:

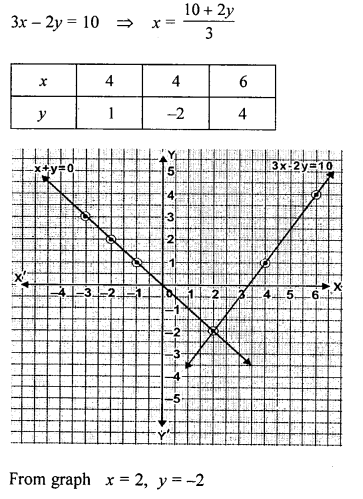
Question 4.
Take 1 cm to represent 1 unit on each axis to draw the graphs of the equations 4x- 5y = -4 and 3x = 2y – 3 on the same graph sheet (same axes). Use your graph to find the solution of the above simultaneous equations.
Solution:
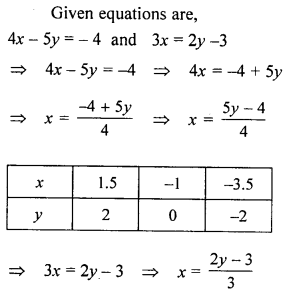
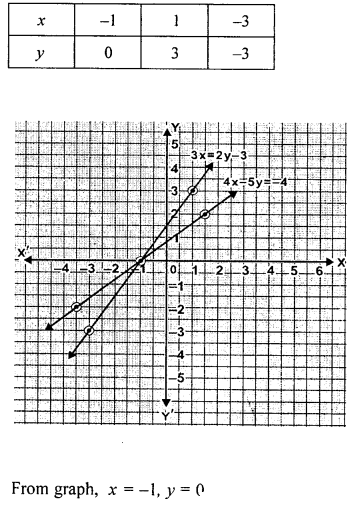
Question 5.
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically, x + 3y = 8, 3x = 2 + 2y
Solution:
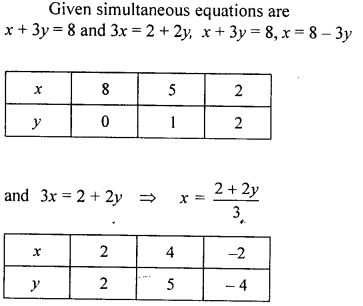
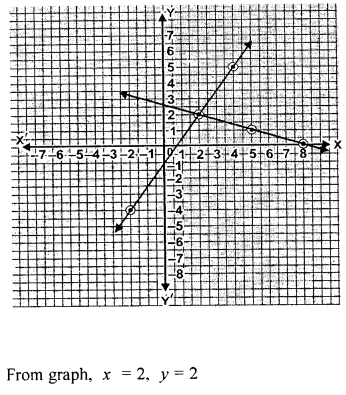
Question 6.
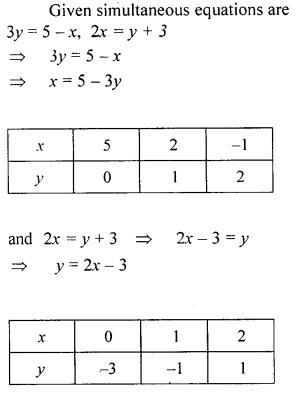
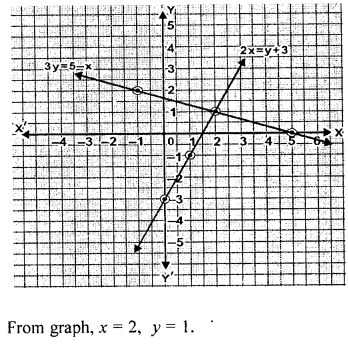
Solve graphically the simultaneous equations 3y = 5 – x, 2x = y + 3 (Take 2cm = 1 unit on both axes).
Solution:
Question 7.
Use graph paper for this question.
Take 2 cm = 1 unit on both axes.
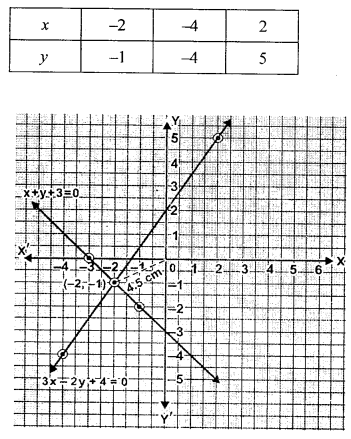
(i) Draw the graphs of x +y + 3 = 0 and 3x-2y + 4 = 0. Plot only three points per line.
(ii) Write down the co-ordinates of the point of intersection of the lines.
(iii) Measure and record the distance of the point of intersection of the lines from the origin in cm.
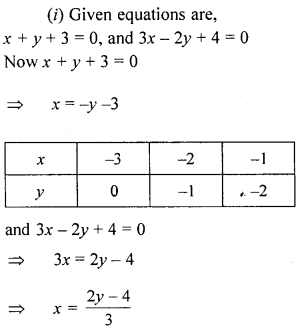
Solution:
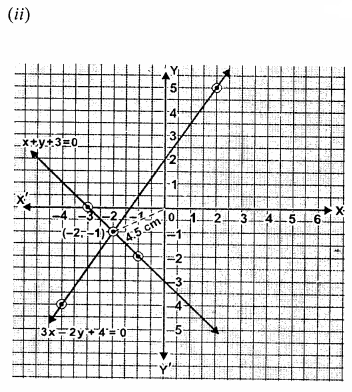

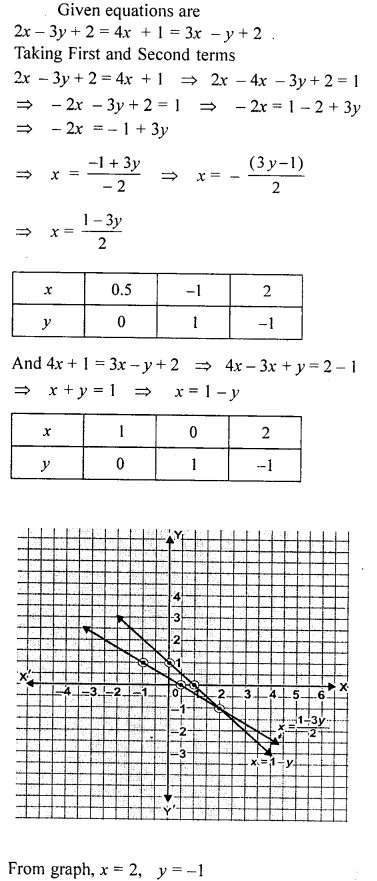
Question 8.
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically :
2x-3y + 2 = 4x+ 1 = 3x – y + 2
Solution:
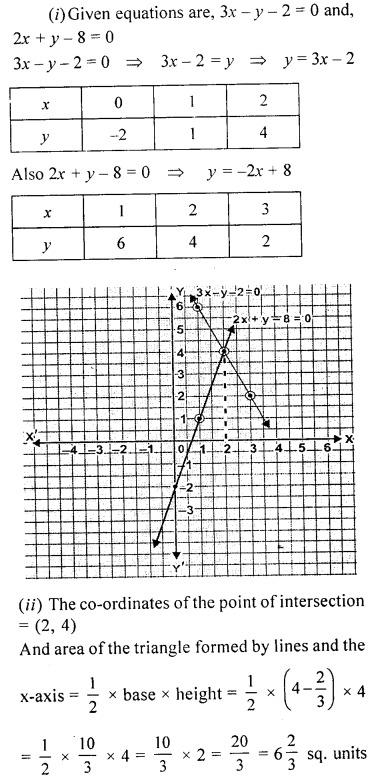
Question 9.
Use graph paper for this question.
(i) Draw the graphs of 3x -y – 2 = 0 and 2x + y – 8 = 0. Take 1 cm = 1 unit on both axes and plot three points per line.
(ii) Write down the co-ordinates of the point of intersection and the area of the traingle formed by the lines and the x-axis.
Solution:
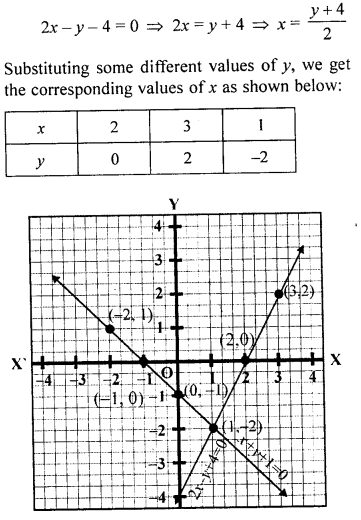
Question 10.
Solve the following system of linear equations graphically : 2x -y – 4 = 0, x + y + 1 = 0. Hence, find the area of the triangle formed by these lines and the y-axis.
Solution:

Question 11.
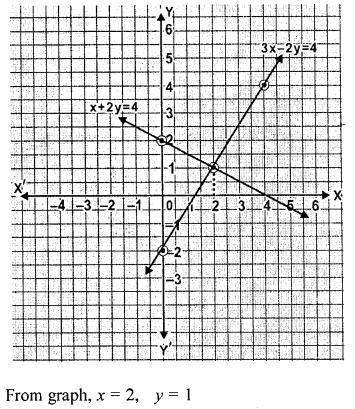
Solve graphically the following equations: x + 2y = 4, 3x – 2y = 4
Take 2 cm = 1 unit on each axis. Write down the area of the triangle formed by the lines and the x-axis.
Solution:
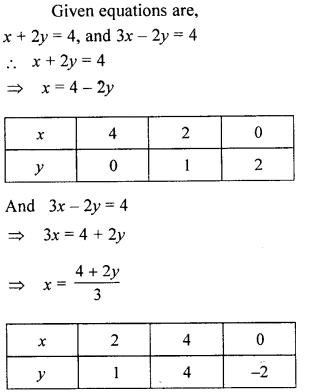
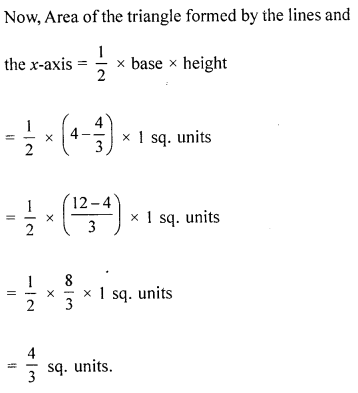
Question 12.
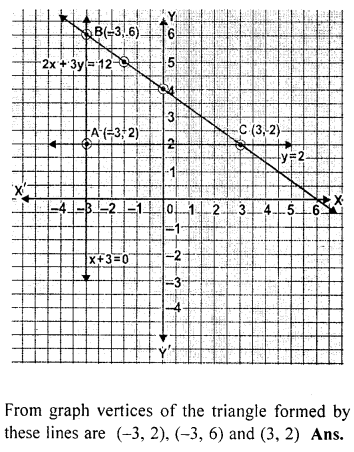
On graph paper, take 2 cm to represent one unit on both the axes, draw the lines : x + 3 = 0, y – 2 = 0, 2x + 3y = 12 .
Write down the co-ordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines.
Solution:
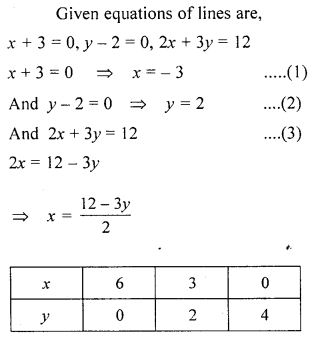
Question 13.
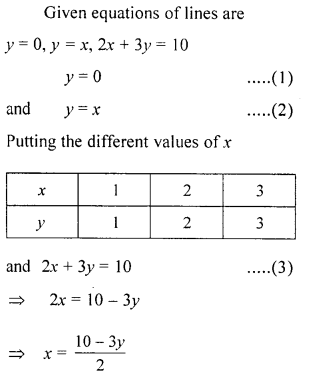
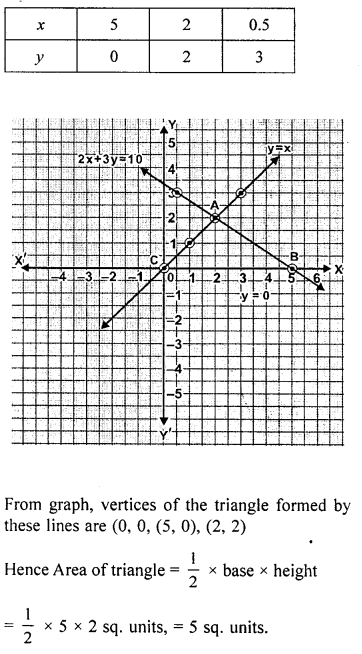
Find graphically the co-ordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by the lines y = 0, y – x and 2x + 3y= 10. Hence find the area of the triangle formed by these lines.
Solution:
EXERCISE 19.4
Question 1.
Find the distance between the following pairs of points :
(i) (2, 3), (4, 1)
(ii) (0, 0), (36, 15)
(iii) (a, b), (-a, -b)
Solution:
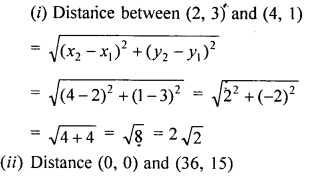
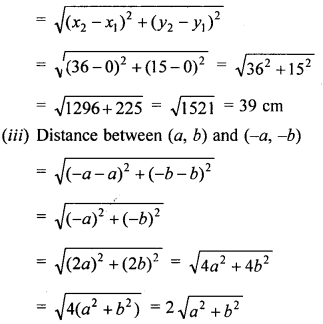
Question 2.
A is a point on y-axis whose ordinate is 4 and B is a point on x-axis whose abscissa is -3. Find the length of the line segment AB.
Solution:
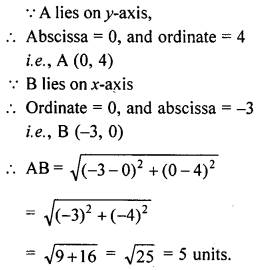
Question 3.
Find the value of a, if the distance between the points A (-3, -14) and B (a, -5) is 9 units.
Solution:
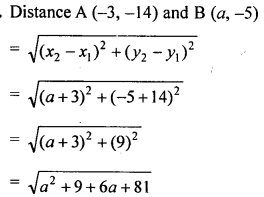
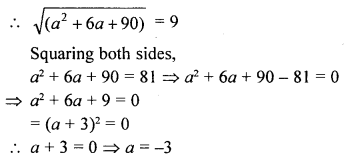
Question 4.
(i) Find points on the x-axis which are at a distance of 5 units from the point (5, -4).
(ii) Find points on the y-axis are at a distance of 10 units from the point (8, 8) ?
(iii) Find points (or points) which are at a distance of √10 from the point (4, 3) given that the ordinate of the point or points is twice the abscissa.
Solution:


Question 5.
Find the point on the x-axis which, is equidistant from the points (2, -5) and (-2, 9).
Solution:

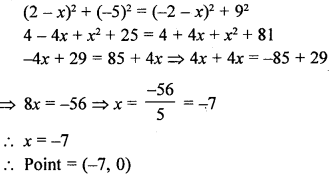
Question 6.
Find the value of x such that PQ = QR where the coordinates of P, Q and R are (6, -1), (1, 3) and (x, 8) respectively.
Solution:

Question 7.
If Q (0, 1) is equidistant from P (5, -3) and R (x, 6) find the values of x.
Solution:

Question 8.
Find a relation between x and y such that the point (x, y) is equidistant from the points (7, 1) and (3, 5).
Solution:
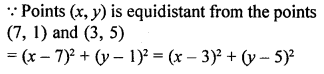
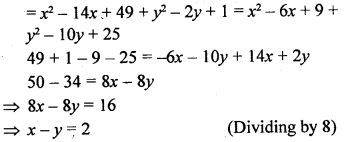
Question 9.
The x-coordinate of a point P is twice its y-coordinate. If P is equidistant from the points Q (2, -5) and U (-3, 6), then find the coordinates of P.
Solution:

Question 10.
If the points A (4,3) and B (x, 5) are on a circle with centre C (2, 3), find the value of x.
Solution:

Question 11.
If a point A (0, 2) is equidistant from the points B (3, p) and C (p, 5), then find the value of p.
Solution:
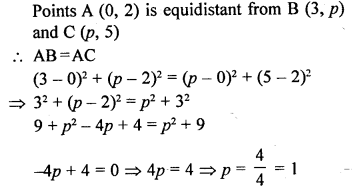
Question 12.
Using distance formula, show that (3, 3) is the centre of the circle passing through the points (6, 2), (0, 4) and (4, 6).
Solution:

Question 13.
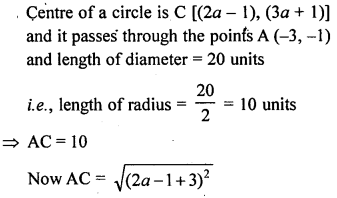
The centre of a circle is C (2α – 1, 3α + 1) and it passes through the point A (-3, -1). If a diameter of the circle is of length 20 units, find the value(s) of α.
Solution:
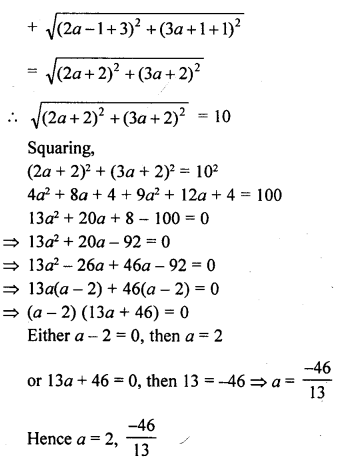
Question 14.
Using distance formula, show that the points A (3, 1), B (6, 4) and C (8, 6) are coliinear.
Solution:

Question 15.
Check whether the points (5, -2), (6, 4) and (7, -2) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
Solution:

Question 16.
Name the type of triangle formed by the points A (-5, 6), B (-4, -2) and (7, 5).
Solution:

Question 17.
Show that the points (1, 1), (- 1, – 1) and (-√3,√3) form an equilateral triangle.
Solution:
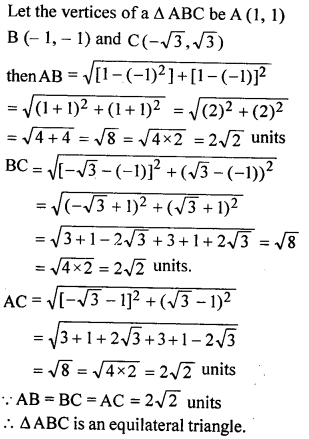
Question 18.
Show that the points (7, 10), (-2, 5) and (3, -4) are the vertices of an isosceles right triangle.
Solution:

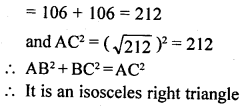
Question 19.
The points A (0, 3), B (- 2, a) and C (- 1, 4) are the vertices of a right angled triangle at A, find the value of a.
Solution:

Question 20.
Show that the points (0, – 1), (- 2, 3), (6, 7) and (8, 3), taken in order, are the vertices of a rectangle. Also find its area.
Solution:

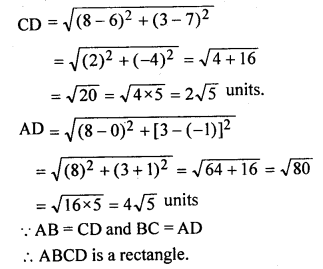
Question 21.
If P (2, -1), Q (3, 4), R (-2, 3) and S (-3, -2) be four points in a plane, show that PQRS is a rhombus but not a square. Find the area of the rhombus.
Solution:


Question 22.
Prove that the points A (2, 3), B {-2, 2), C (-1, -2) aqd D (3, -1) are the vertices of a square ABCD.
Solution:
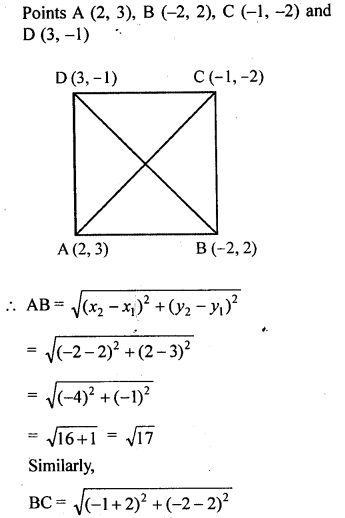
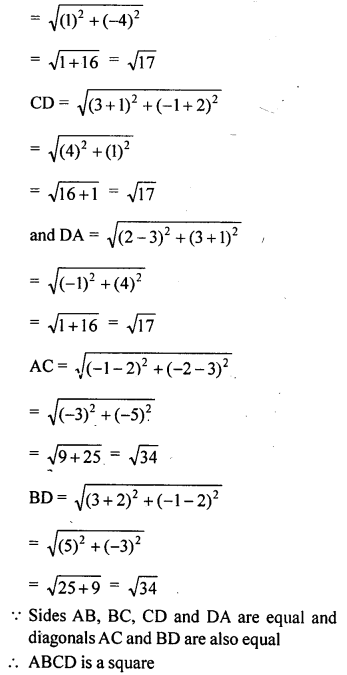
Question 23.
Name the type of quadrilateral formedby the following points and give reasons for your answer :
(i) (-1, -2), (1, 0), (-1, 2), (-3, 0)
(ii) (4, 5), (7, 6), (4, 3), (1, 2)
Solution:
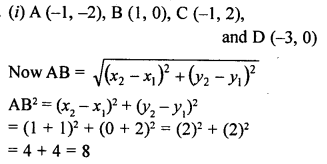



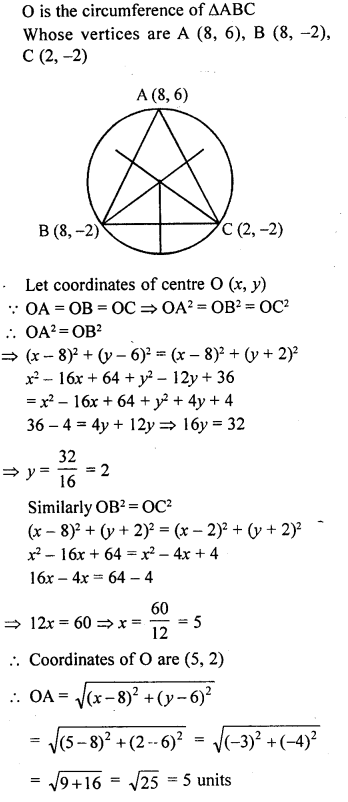
Question 24.
Find the coordinates of the circumcentre of the triangle whose vertices are (8, 6), (8, -2) and (2, -2). Also, find its circumradius.
Solution:
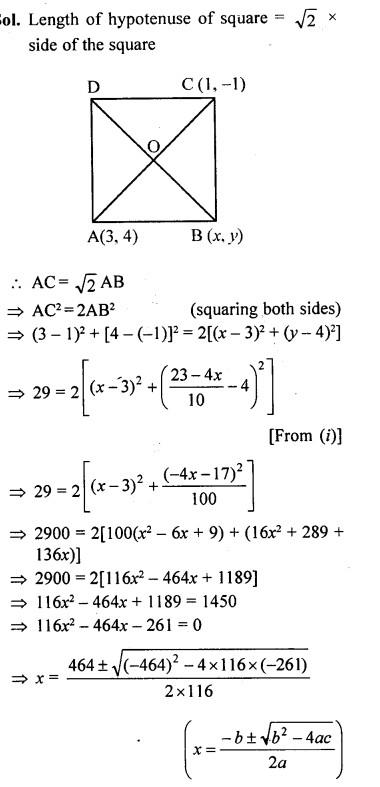
Question 25.
If two opposite vertices of a square are (3, 4) and (1, -1), find the coordinates of the other two vertices.
Solution:
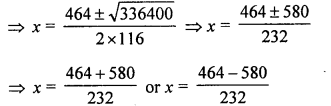

Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1 to 16):
Question 1.
Point (-3, 5) lies in the
(a) first quadrant
(b) second quadrant
(c) third quadrant
(d) fourth quadrant
Solution:
Point (-3, 5) lies in second quadrant, (b)
Question 2.
Point (0, -7) lies
(a) on the x-axis
(b) in the second quadrant
(c) on the y-axis
(d) the fourth quadrant
Solution:
Point (0, -7) lies on y-axis (as x = 0) (c)
Question 3.
Abscissa of a point is positive in
I and II quadrants
I and IV quadrants
I quadrant only
II quadrant only
Solution:
Abscissa of a point is positive in first and fourth quadrants. (b)
Question 4.
The point which lies ony-axis at a distance of 5 units in the negative direction of y- axis is
(a) (0, 5)
(b) (5, 0)
(c) (0, -5)
(d) (-5, 0)
Solution:
(0, -5) is the required point. (c)
Question 5.
If the perpendicular distance of a point P from the x-axis is 5 units and the foot of perpendicular lies on the negative direction of x-axis, then the point P has
(a) x-coordinate = -5
(b) y-coordinate = 5 only
(c) y-coordinate = -5 only
(d) y-coordinate = 5 or -5
Solution:
Perpendicular distance for a point P on x- axis in negative direction.
It will has y = 5 and x = -5 (d)
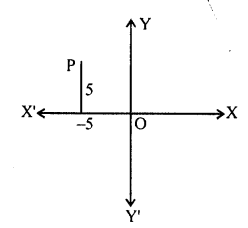
Question 6.
The points whose abscissa and ordinate have different signs will lie in
(a) I and II quadrants
(b) II and III quadrants
(c) I and III quadrants
(d) II and IV quadrants
Solution:
Point which has abscissa and ordinate having different signs will lie in second and fourth quadrants. (d)
Question 7.
The points (-5, 2) and (2, -5) lie in
(a) same quadrant
(b) II and III quadrants respectively
(c) II and IV quadrants respectively
(d) IV and II quadrants respectively
Solution:
Points (-5, 2) and (2, -5) lie in second and fourth quadrants respectively. (b)
Question 8.
If P (-1,1), Q (3, -4), R (1, -1), S (-2, -3) and T (-4, 4) are plotted on the graph paper, then point(s) in the fourth quadrant are
(a) P and T
(b) Q and R
(c) S only
(d) P and R
Solution:
Points P (-1, 1), Q (3, -4), R (1, -1), S (-2, -3) and T (-4, 4) are plotted on graph The points in 4th quadrant are Q and R (b)
Question 9.
On plotting the points O (0, 0), A (3, 0), B (3, 4), C (0, 4) and joining OA, AB, BC and CO which of the following figure is obtained?
(a) Square
(b) Rectangle
(c) Trapezium
(d) Rhombus
Solution:
On plotting the points O (0, 0), A (3, 0), B (3, 4), C (0, 4)
OA, AB, BC and CO are joined
The figure so formed will a rectangle (b)
Question 10.
Which of the following points lie on the graph of the equation :
3x-5y + 7 = 0?
(a) (1, -2)
(b) (2, 1)
(c) (-1, 2)
(d) (1, 2)
Solution:

Question 11.
The pair of equation x – a and y = b graphically represents lines which are
(a) parallel
(b) intersecting at (b, a)
(c) coincident
(d) intersecting at (a, b)
Solution:
x = a, y = 6
Which are intersecting at (a, b) (d)
Question 12.
The distance of the point P (2, 3) from the x>axis is
(a) 2 units
(b) 3 units
(c) 1 unit
(d) 5 units
Solution:
The distance of the point P (2, 3) from x- axis is 3 units (as y = 3). (b)
Question 13.
The distance of the point P (-4, 3) from the y-axis is
(a) 5 units
(b) -4 units
(c) 4 units
(d) 3 units
Solution:
The distance of the point P (-4, 3) from y- axis will be 4 units. (c)
Question 14.
The distance of the point P (-6, 8) from the origin is
(a) 8 units
(b) 2\(\sqrt { 7 }\) units
(c) 10 units
(d) 6 units
Solution:
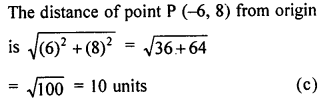
Question 15.
The distance between the points A (0, 6) and B (0, -2) is
(a) 6 units
(b) 8 units
(c) 4 units
(d) 2 units
Solution:
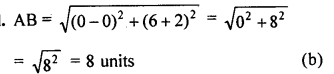
Question 16.
The distance between the points (0, 5) and (-5, 0) is
(a) 5 units
(b) 5\(\sqrt { 2 }\)units
(c) 2 \(\sqrt { 7 }\) units
(d) 10 units
Solution:
The distance between the points (0, 5) and (-5, 0) is
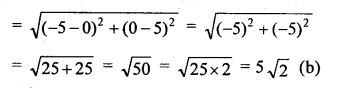
Question 17.
AOBC is a rectangle whose three vertices are A (0, 3), O (0, 0) and B (5, 0). The length of its diagonal is
(a) 5 units
(b) 3 units
(c) \(\sqrt { 34 }\) units
(d) 4 units
Solution:
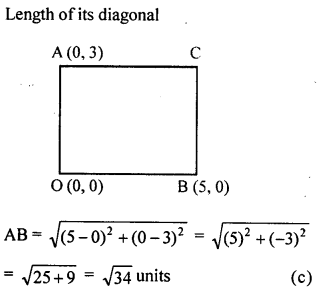
Question 18.
If the distance between the points (2, -2) and (-1, x) is S units, then one of the value of x is
(a) -2
(b) 2
(c) -1
(d) 1
Solution:

![]()
Question 19.
The distance between the points (4, p) and (1, 0) is 5 units, then the value of p is
(a) 4 only
(b) -4 only
(c) ±4
(d) 0
Solution:

Question 20.
The points (-4, 0), (4, 0) and (0, 3) are the vertices of a
(a) right triangle
(b) isosceles triangle
(c) equilateral triangle
(d) scalene triangle
Solution:

Question 21.
The area of a square whose vertices are A (0, -2), B (3, 1), C (0, 4) and D (-3, 1) is
(a) 18 sq. units
(b) 15 sq. units
(c) \(\sqrt { 18 }\) sq. units
(d) \(\sqrt { 15 }\) sq. units
Solution:
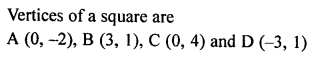
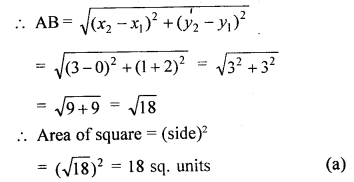
Question 22.
In the given figure, the area of the triangle ABC is
(a) 15 sq. units
(b) 10 sq. units
(c) 7.5 sq. units
(d) 2.5 sq. units
Solution:
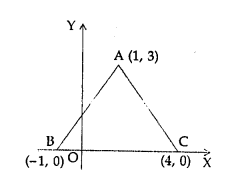

Question 23.
The perimeter of a triangle with vertices (0, 4), (0, 0) and (3, 0) is
(a) 5 units
(b) 12 units
(c) 11 units
(d) 7 + \(\sqrt { 5 }\) units
Solution:

Question 24.
If A is a point on the .y-axis whose ordinate is 5 and B is the point (-3, 1), then the length of AB is
(a) 8 units
(b) 5 units
(c) 3 units
(d) 25 units
Solution:
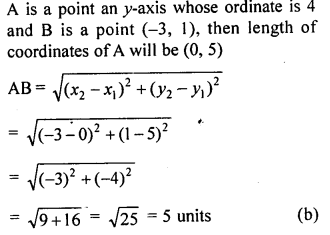
Question 25.
The point A (9, 0), B (9, 6), C (-9, 6) and D (-9, 0) are the vertices of a
(a) rectangle
(b) square
(c) rhombus
(d) trapezium
Solution:

Chapter Test
Question 1.
Three vertices of a rectangle are A (2, -1), B (2, 7) and C(4, 7). Plot these points on a graph and hence use it to find the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex D Also find the co-ordinates of
(i) the mid-point of BC
(ii) the mid point of CD
(iii) the point of intersection of the diagonals. What is the area of the rectangle ?
Solution:
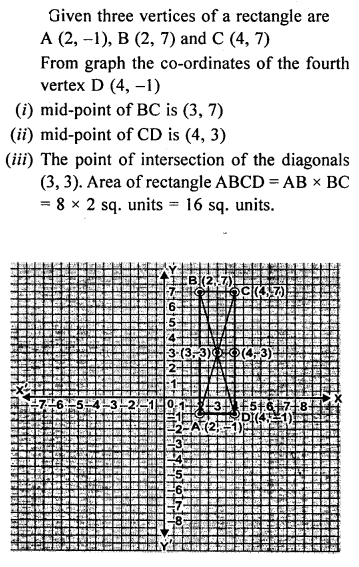
Question 2.
Three vertices of a parallelogram are A (3, 5), B (3, -1) and C (-1, -3). Plot these points on a graph paper and hence use it to find the coordinates of the fourth vertex D. Also find the coordinates of the mid-point of the side CD. What is the area of the parallelogram?
Solution:
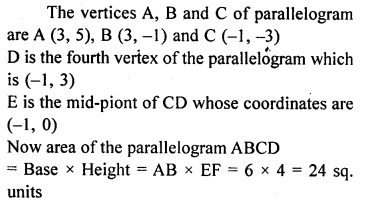
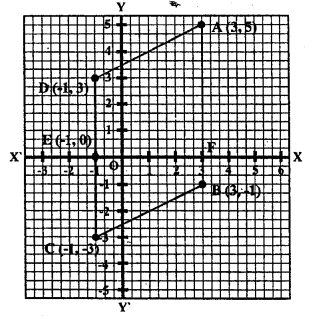
Question 3.
Draw the graphs of the following linear equations.
(i) y = 2x – 1
(ii) 2x + 3y = 6
(iii) 2x – 3y = 4.
Also find slope and y-intercept of these lines.
Solution:
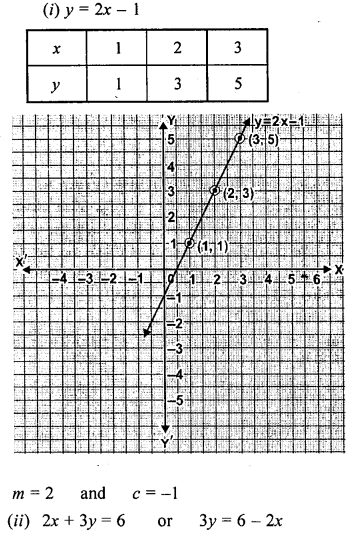
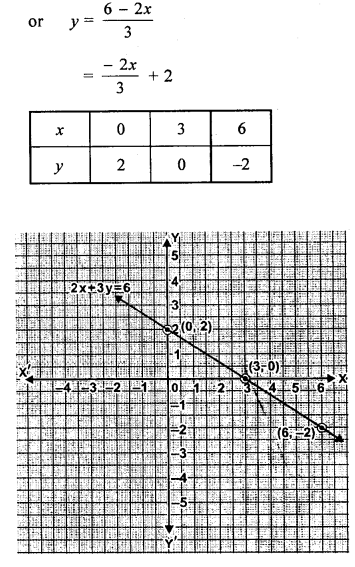
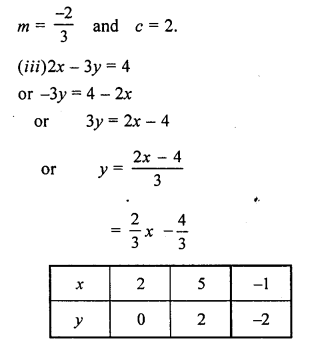
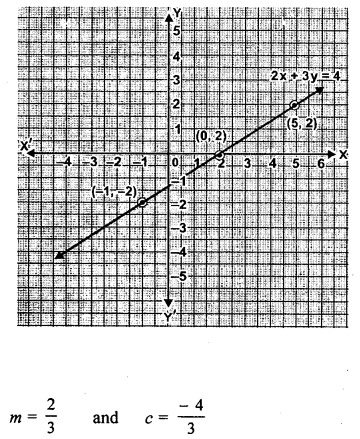
Question 4.
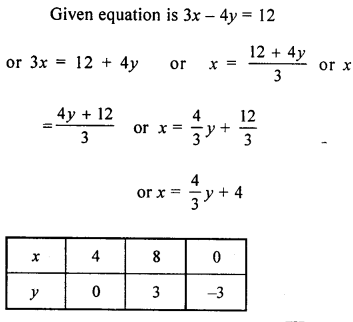
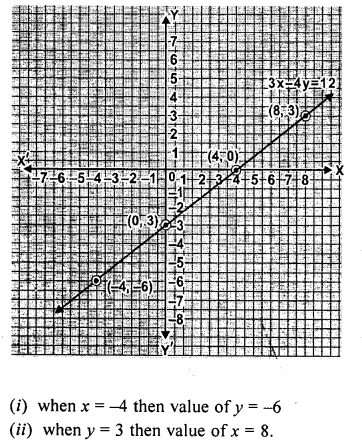
Draw the graph of the equation 3x – 4y = 12. From the graph, find :
(i) the value of y when x = -4
(ii) the value of x when y = 3.
Solution:
Question 5.
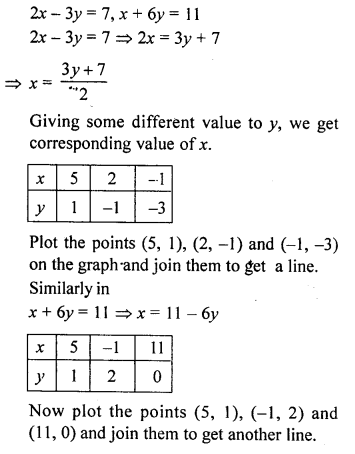
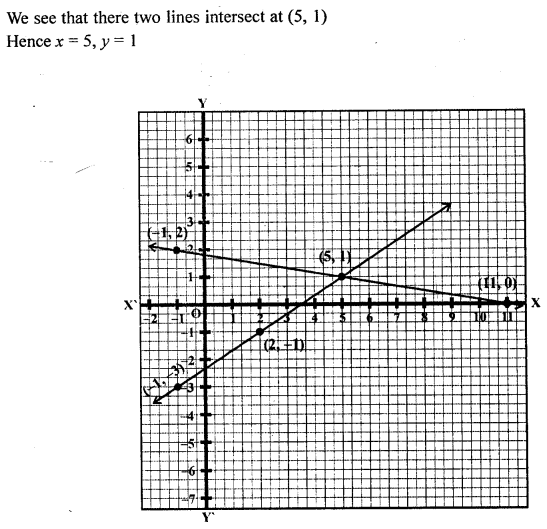
Solve graphically, the simultaneous equations: 2x – 3y = 7; x + 6y = 11.
Solution:
Question 6.
Solve the following system of equations graphically: x – 2y – 4 = 0, 2x + .y – 3 = 0.
Solution:

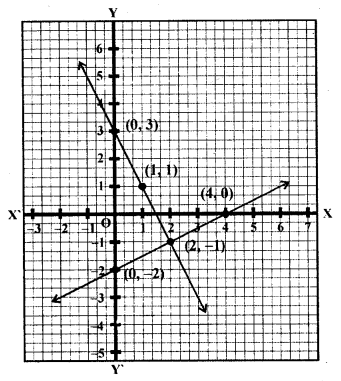
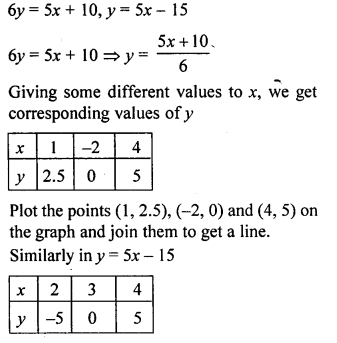
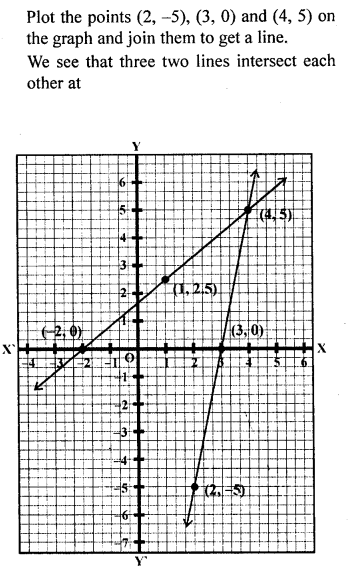
Question 7.
Using a scale of l cm to 1 unit for both the axes, draw the graphs of the following equations : 6y = 5x:+ 10,y = 5;c-15. From the graph, find
(i) the coordinates of the point where the two lines intersect.
(ii) the area of the triangle between the lines and the x-axis.
Solution:
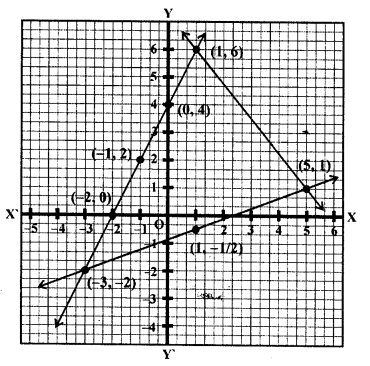
Question 8.
Find, graphically, the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by the lines : 8y – 3x + 7 = 0, 2x-y + 4 = 0 and 5x + 4y = 29.
Solution:


Question 9.
Find graphically the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by the lines y-2 = 0,2y + x = 0 and y + 1 = 3(x – 2). Hence, find the area of the triangle formed by these lines.
Solution:

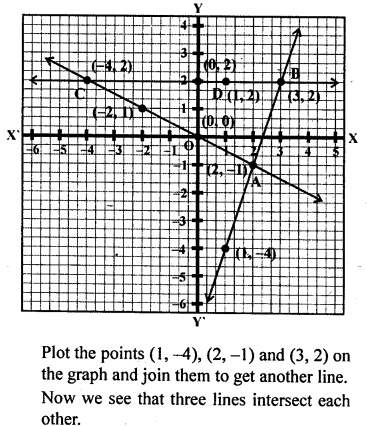
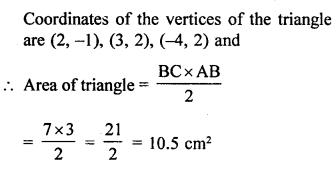
Question 10.
A line segment is of length 10 units and one of its end is (-2,3). If the ordinate of the other end is 9, find the abscissa of the other end.
Solution:
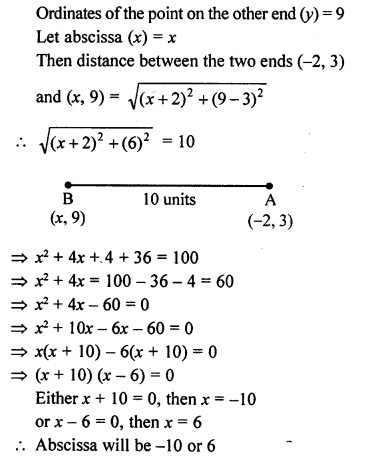
Question 11.
A (-4, -1), B (-1, 2) and C (a, 5) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle. Find the value of a, given that AB is the unequal side.
Solution:
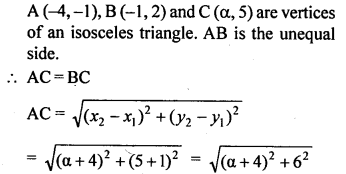
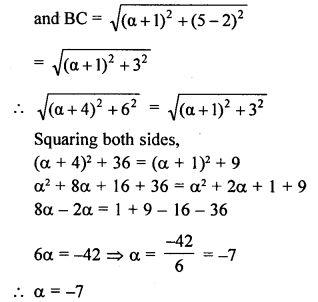
Question 12.
If A (-3, 2), B (a, p) and C (-1, 4) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle, prove that α + β = 1, given AB = BC.
Solution:

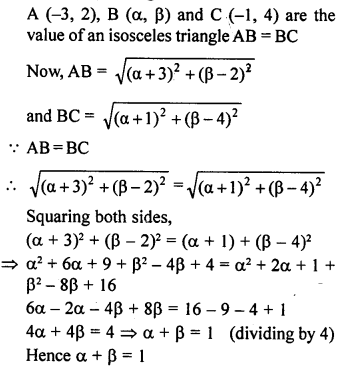
Question 13.
Prove that the points (3, 0), (6, 4) and (-1, 3) are the vertices of a right angled isosceles triangle.
Solution:
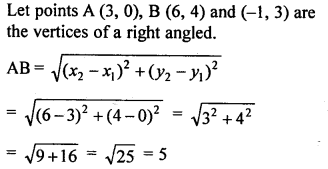

Question 14.
(i) Show that the points (2, 1), (0,3), (-2, 1) and (0, -1), taken in order, are the vertices of a square. Also find the area of the square.
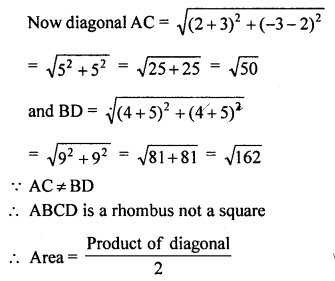
(ii) Show that the points (-3, 2), (-5, -5), (2, -3) and (4, 4), taken in order, are the vertices of rhombus. Also find its area. Do the given points form a square?
Solution:
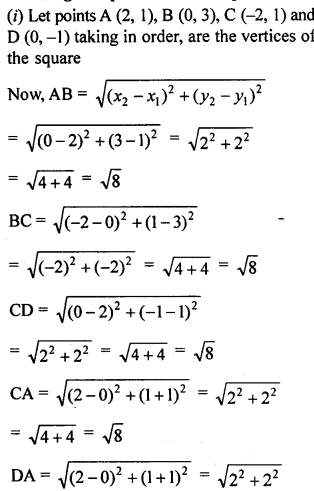
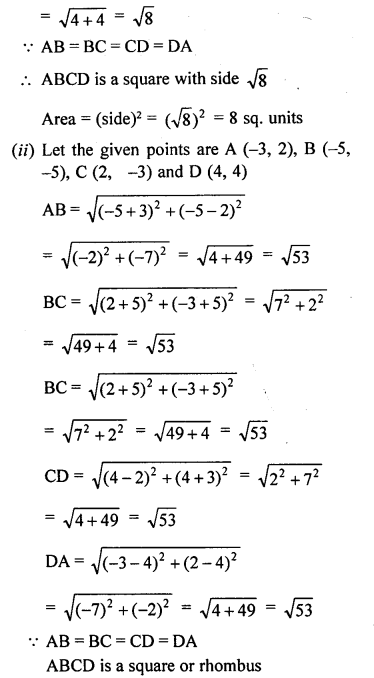
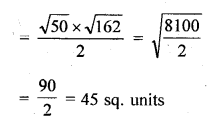
Question 15.
The ends of a diagonal of a square have co-ordinates (-2, p) and (p, 2). Find p if the area of the square is 40 sq. units.
Solution:

Question 16.
What type of quadrilateral do the points A (2, -2), B (7, 3), C (11, -1) and D (6, -6), taken in the order, form?
Solution:
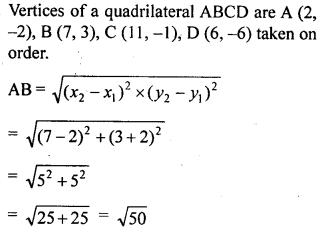
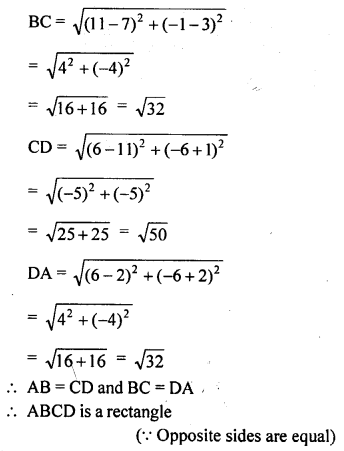
Question 17.
Find the coordinates of the centre of the circle passing through the three given points A (5, 1), B (-3, -7) and C (7, -1).
Solution: