Reflection at Plane Surface Formulas
Fed up looking everywhere for help regarding the Concept Reflection at Plane Surface? You need not worry anymore as we have come up with the complete list of Reflection at Plane Surface Formulas. Utilize the Cheat Sheet of Reflection at Plane Surface and try to memorize the formulae as you might need them at some point. Try seeking help regarding various concepts of Physics you feel difficult from Physics Formulas. Reflect at Plane Surface Formulae includes Laws of reflection, Characteristics of Reflection at Plane Mirror, etc.
Formulae Sheet of Reflection at Plane Surface
A. Law’s of reflection
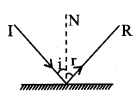
I law → ∠i = ∠r
II law → I, R & N are in a same plane.
Note → These laws are also valid for all types of surfaces (curved, plane, smooth, rough etc.)
B. Important point
- Light propagates in straight lines in homogeneous media.
- Rays do not disturb each other upon intersection.
- Rays retrace their path when their direction is reversed.
C. Characteristics of reflection at plane mirror
1. The image is always of same size and at same distance behind the mirror as the object in front of it.
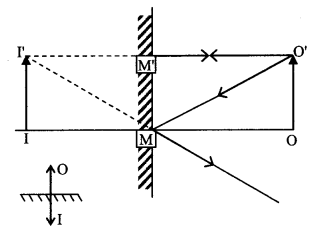
2. When the object is real, virtual image is formed and vice – versa.
3. The image is always erect when the object is in front of the mirror but inverted when the object is above the mirror.
4. As every part of mirror forms complete image of an extended object and due to superposition of images brightness will depend on the light reflecting area of the mirror. [It can be explained by Huygen’s principle.]
5. Though every part of a mirror forms complete image of an object, we usually see only that part of image from which light after reflection from the mirror reaches our eye.
6. Deviation δ is defined as the angle between directions of incident ray and emergent ray. So if light is incident at an angle of incidence i,
δ = π – (i + r) = π -2i
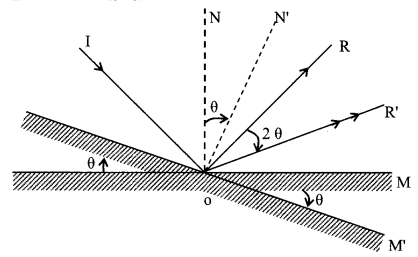
7. If keeping the incident ray fixed, the mirror is rotated by an angle θ, about an axis in the plane of mirror. The reflected ray is rotated through an angle 2θ
8. If object moves towards the plane mirror at speed v, the image moves towards the plane mirror at speed – v. So, the image speed w.r.t object is – v – v = – 2v
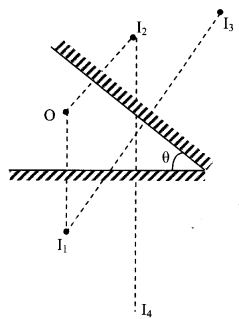
9. When two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle θ and an object is placed in between them due to multiple reflections more than one image are formed. This number of image n is either \(\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}\) or \(\left(\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1\right)\) accordingly as \(\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}\) is odd or even respectively.
Again if \(\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}\) is odd and the object is place symmetrically between two mirrors, then final two images coincide and there by leaving \(\left(\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1\right)\)
10. Minimum height of a mirror where a man of height H can see his full image is \(\frac{\mathrm{H}}{2}\)
11. Net Angle of deviation (δ) of a ray from two plane mirrors inclined an angle θ.
δ = 2π – θ
12. Size of the mirror (h) to see full image of a wall of height H by an observer standing as given figure.
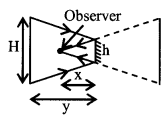
h = \(\frac{x}{x+y}\) H
If observer standing at mid-way between the wall and the mirror then 1/3 size of mirror required to see full image of the wall.
If you are looking for instant help on several Physics concepts and their related formulas & cheat sheets Onlinecalculator.guru is the place for you.