Salt Analysis Formulas
Analytical Chemistry is one of the important parts of the chemistry subject as it deals with qualitative analysis of inorganic compounds. So, get a grip on the concept of salt analysis by using the list of salt analysis formulas provided over here. By referring to the Salt Analysis Formulae Sheet, students can easily memorize the concept formulas and apply them whenever required during the calculations. Once take a look at the below complete list of Salt Analysis Formulas and Salt Analysis Formulae Tables & ace up your subject learnings.
Solve your chemistry problems fastly and efficiently taking the help of Chemistry Formulas and learn about the Concepts without much effort.
Salt Analysis Formulae Cheat Sheet | Tables for Salt Analysis Formulas
Want to get familiar with all concept formulas of salt analysis? then referring to the provided list of salt analysis formulas is the best option for all students who are preparing for the chemistry exam. Do memorize all these formulas of sat analysis and apply them correctly during the calculations. Stick to this page and avail full list of Salt Analysis Formulas from here without any fail.
Analytical chemistry involves qualitative analysis of inorganic compounds.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF SALTS
| OBSERVATION | INFERENCE |
| 1. Substance is coloured
(a) Light pink |
Hydrated salt of Mn |
| (b) Reddish pink | Hydrated salt of Co (II) |
| (c) Red | HgO, Hgl2, Pb3O4, |
| (d) Orange red | Sb2S3, some dichromates and ferricyanides |
| (e) Reddish brown | Fe2O3 |
| (f) Dark brown | PbO2, Bi2S3 CdO, Ag2O, CuCrO4, SnS |
| (g) Light Yellow or brown | Chromates, As2S3, As2S5, AgBr, Agl, PbI2 CdS, SnS2, a few iodides and ferrocyanides |
| (h) Green | K2MnO4, Ni salts, hydrated ferrous salts, some Cu (II) Compounds |
| (i) Dark green | Salt of Cr (III) |
| (j) Blue | Hydrated CuSO4, Anhydrous CaSO4 |
| (k) Black | Sulphides of Ag(I), Cu(I), Cu(II), Fe(II), Ni(II), Co(II) Hg(II), and Pb(II), Mn02, Fe3O4, FeO, CuO, Co3O4, Ni2O3 |
| (l) Light yellow or brown | Ferric salts |
| 2. Substance smells (a) Ammoniacal smell |
Ammonium carbonates and other ammonium salts. |
| (b) Bitter almond type | Cyanides |
| (c) Vinegar or acetic acid type | Acetates |
| (d) Chlorine gas smell | Hypochlorites |
| 3. Solution is coloured (a) Green or blue |
Ni2+. Fe2+, Cr3+, and Cu2+ |
| (b) Pink | Co2+ and Mn2+ |
| (c) Yellow | CrO42- Fe3+, [Fe(CN)6]4- |
| (d) Orange or purple | Dichromates (orange), permanganates (purple) |
| 4. Substance is heavy | Salts of Pb, Hg and Ba |
| 5. Substance is light | Carbonates of Mg, Al, Zn, Ca, Sr, Bi |
| 6. Substance is wet | ZnCl2, MgCl2, MnCl2, nitrites, nitrates, CaCl2 |
| 7. Insoluble precipitates which are insoluble in cone, acids | |
| (a) White | BaSO4, SrSO4, PbSO4, CaF2, AgCl, SnO2, Sb2O4 and Al2O3 |
| (b) Yellow | AgBr, Agl, BaCrO4 |
| Green | CrO3, Cr2(SO4)3 |
| Black | HgS |
| Violet | CrCl3 |
| Dark red | Fe2O3 |
HEATING EFFECTS ON VARIOUS SALTS
| OBSERVATION | INFERENCE |
| 1. Substance decrepitates (crackling noise) | NaCl, KI, Pb(NO3)2, Ba(NO3)2 |
| 2. Substance melts | Salts of alkali metals and salts having water of crystallization |
| 3. Substance swells (due to loss of water of crystallizations) | Alums, borates and phosphates |
| 4. The substance sublimes and the colour of sublimate is- (a) White (b) Yellow (c) Blue black and violet vapours |
Hg2Cl2, NH4X, AlCl3, HgCl2, As2O3, Sb2O3 |
| 5. A residue (generally oxides) is left & its colour is- (a) Yellow (hot) and White (cold) (b) Reddish Brown (hot); Yellow (cold) (c) Black (hot); Red (cold) (d) Black (hot) ; Red Brown (cold) |
ZnO PbO HgO, Pb3O4 Fe2O3 |
| 6. Gas is evolved – (i) Colourless & odourless (a) CO2 – turns lime water milky (b) O2 – rekindles a glowing splinter (c) N2 – (Inactive) |
Carbonates and oxalates (CaCO3 → CaO + CO2) Alkali nitrates (2KNO3 → 2KNO2 + O2) Ammonium nitrite (NH4NO2 → N2 + 2H2O) |
| (ii) Colourless gas with odour – (a) NH3 – turns red litmus blue and mercurous nitrate paper black (b ) SO2 – Smell of burning sulphur, turns acidified K2Cr2O7 paper green (c) HCl-Pungent smell, white fumes with ammonia (d) H2S – Smell of rotten eggs, turns lead acetate paper black |
Ammonium salts (NH4)2SO4 → NH4HSO4 + NH, Sulphites and thiosulphates CaSO3 → CaO – SO2 Hydrated chlorides CaCl2.6H2O → Ca(OH)2 + 4H2O + 2HCl Sulphides Na2S + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2S |
| (iii) Coloured gas – (A) NO2 – Brown, turns starch iodide paper blue (B) Br2 – Reddish Brown (a) turns starch paper yellow (b) turns starch iodide paper blue (C) I2 – Violet, turns starch paper blue (D) Cl2 – Greenish yellow, (a) bleaches moist litmus paper (b) bleaches indigo solution (c) turns starch iodide paper blue |
Nitrites and nitrates of heavy metals 2Cu (NO3)2 → 2CuO + 4NO2+ O2 Bromides 2 CdBr2 + O2 → 2CdO + 2Br2 Iodides 2CdI2 + O2 → 2CdO + 2I2 Chlorides CuCl2 + H2O → CuO + 2HCl CuO + 2HCl → Cu + H2O + Cl2 |
SEPARATION OF BASIC RADICALS INTO GROUPS
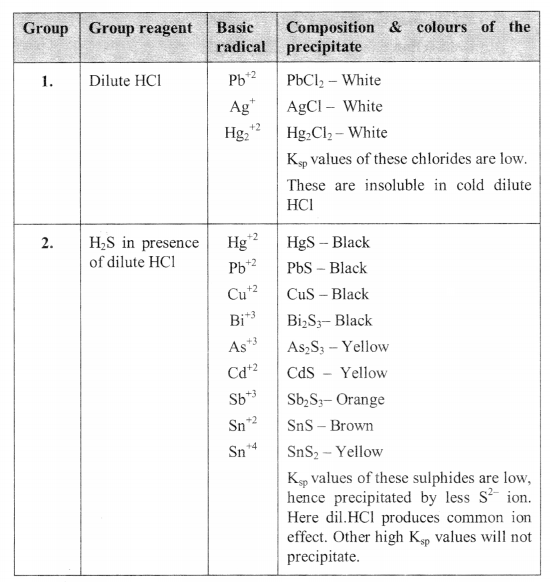
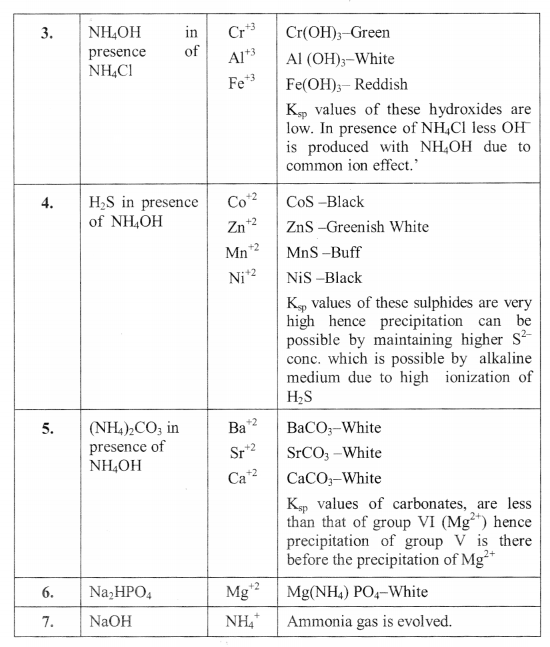
DRY TESTS:
These tests give clear indication of the presence of certain radicals –
Flame test
| Colour of Flame | Inference |
| Pale greenish | Pb |
| Green with a blue centre | Cu |
| Apple green | Ba |
| Crimson red | Sr, Li |
| Brick red | Ca |
| Pink-violet (Lilac) | K |
| Golden yellow | Na |
| Violet | Rb, Cs |
| Liquid blue | As, Sb, Bi |
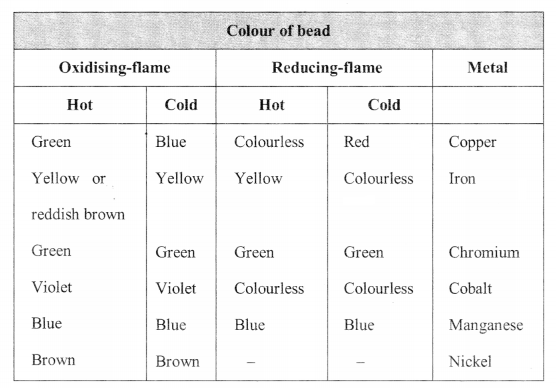
Borax Bead Test:
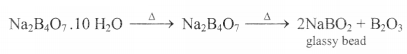
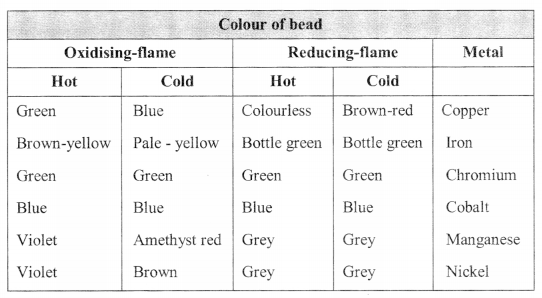
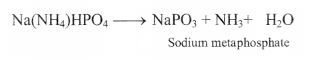
Microcosmic salt bead test:
If you require any support with formulae of various core subjects like Chemistry, Maths, Physics? Go to Onlinecalculator.guru and get the basics easily & efficiently.