X-Ray Formulas
If you need help on the topic X- Rays you have arrived at the right place. The main motto behind providing the X-Ray Formulas is to simplify your calculations. Use the Formula Sheet of X-Rays for quick reference and apply them to your work. Seek any assistance or guidance you need as a part of learning from our Physics Formulas. List of Formulae for X-Rays consists of topics like Characteristic properties of X-Rays, Absorption of X-Rays, Diffraction of X-Rays, etc.
Cheat Sheet for X-Ray
X-rays were discovered by Rongten in 1857, so they are also called Rongton rays.
For the production of X-rays Coolidge tube is used. s
1. Characteristic properties of X-Rays
X-rays are electromagnetic waves. Their hardness depends upon the wavelength or frequency. These rays exhibit reflection, interference, diffraction and polarisation. They affect the photographic plate and produce fluorescence in specific substances. They have ionization power.
2. Absorption of X-Rays
For absorption of X-rays by a substance
![]()
μ → absorption coefficient.
I → Intensity after penetrating x distance.
3. Diffraction of X-Rays
According to Bragg’s law for maxima 2d sin θ = nλ
4. Continuous X-Ray spectrum
When high speed electrons are brought to rest by the numerous collisions with atoms of the target, continuous X-rays are produced. The spectrum contains waves of all wavelengths above a minimum wavelength. This spectrum does not depend the nature of the target.
(a) vmax = \(\frac{\mathrm{eV}}{\mathrm{h}}\) = 0.24 × 1015 V KHz
(b)
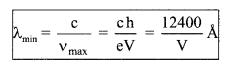
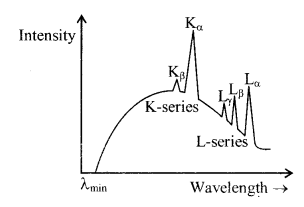
5. Characteristic X-Rays spectrum
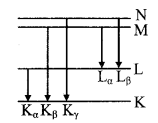
The arrows indicate the transition that give rise to the different series of X-rays
When the high energy electrons knock out electrons from the inner shells K, L, M etc., then transitions of electrons from outer orbits to these vacancies cause the emission of characteristic X-rays. This is a line spectrum and found in the form of various series. This spectrum depends on the nature of the target and its atomic number. For K-series transitions take place from L, M, N ………. Levels to K-level.
(a) W avelength of Kα line
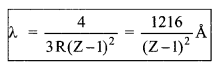
Curve of continuous X-ray and characteristic X-ray.
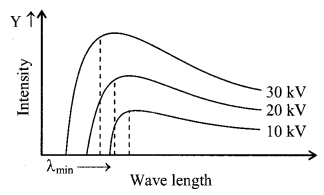
6. Moseley’s law
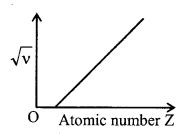
This law relates the frequency of particular lines of characteristic spectrum and the atomic number of the target. According to it, \(\sqrt{v}\) ∝ (Z – σ) where σ is screening constants.
7. Uses of X-Rays
X-rays are used in radiography, X-ray treatment, detection, engineering, trade, laboratory etc.
You can solve any kind of problem easily taking the help of Formula Collection for various concepts of Physics all at one place on Onlinecalculator.guru